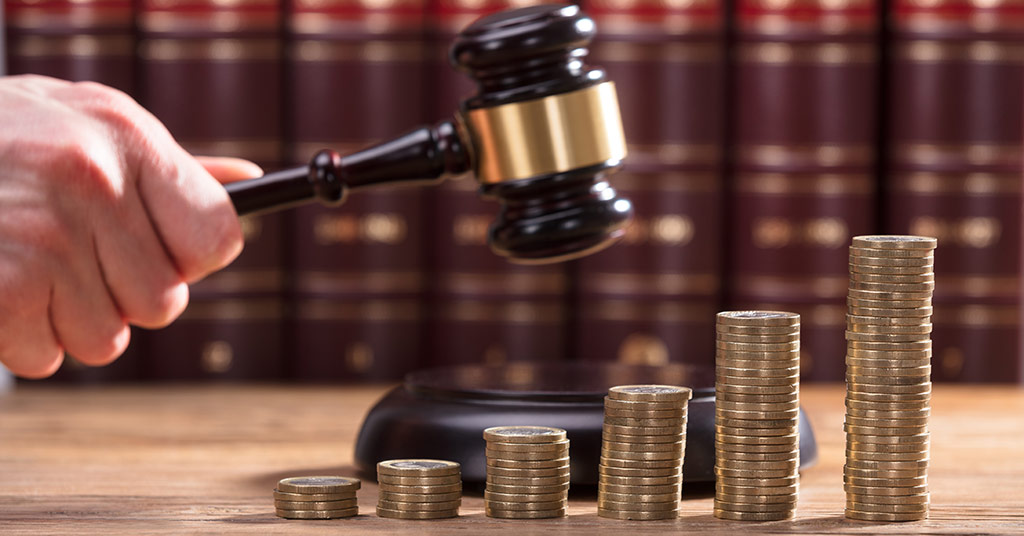
How do attorneys’ contingency fees work in South Africa?

16 Aug 2022
South African legal practitioners may agree to be paid for their services through contingency fees. So how do attorneys’ contingency fees work in South Africa, and are they in your best interests?
In this article, we cover:
- what “contingency fee” means
- how contingency fees work in South Africa
- how contingency fees can benefit clients
- legal limits on lawyers’ contingency fees
What does contingency fee mean?
An attorney’s contingency fee is a charge that’s contingent, or dependent, on the client winning their case. The legal fee is forfeited if the claim isn’t decided in the client’s favour.
A contingency fee model is also sometimes referred to as “no win, no fee”.
How contingency fees work in South Africa
In South Africa, it’s common for personal injury lawyers and their clients to have contingency fee agreements.
A “no-win, no-fee” attorney agrees to cover the costs involved in a case until the case is decided. The attorney also agrees and understands that, if the case is lost, he or she won’t get paid the usual legal fees.
If the attorney wins a client’s case and secures a payout, the agreed contingency fee is paid to the attorney out of the proceeds.
It’s important to note that a contingency fee agreement pertains only to your own attorney’s fees. These aren’t necessarily the only costs involved in pursuing a claim. See Understanding Legal Costs in South Africa: A Simple Guide for an explanation of other costs that may be involved.
How contingency fees benefit legal clients
Many people who need legal services don’t have the money to pay a lawyer upfront.
Contingency fee agreements make it possible for average South Africans to access competent legal advice and representation, without having a lot of funds.
This gives people access to justice, which they otherwise might not have.
No up-front fees to pay
With a contingency fee agreement, there’s nothing to pay your attorney upfront. The attorney agrees to cover the costs when accepting the case.
Added incentive for attorneys
A competent attorney will always act in a client’s best interests, for ethical and professional reasons. Nonetheless, a contingency fee system is an added, financial incentive to win cases.
Waived fees or costs if the case is lost
Legal fees can mount up, especially over the duration of personal injury cases – which may take several years to conclude.
A contingency fee system prevents clients from having to shoulder a burden of debt where cases are not ultimately decided in their favour.
What South African law says about contingency fees
Contingency fee agreements are regulated by the Contingency Fees Act (CFA) 66 of 1997. The Act allows for two alternatives when it comes to contingency fee agreements.
As one alternative, attorneys may claim their normal fees for services rendered – for example, a specified charge per hour – if clients’ claims are successful. This agreement type doesn’t include a statutory cap on the fee amount.
As a second alternative, attorneys may charge a success fee, in addition to their normal fees. The total of both fees may not exceed 25% (including VAT) of the capital sum (damages) recovered or double the lawyer’s normal fees, whichever is the lesser.
Contingency fee agreements that don’t comply with the Act are considered by South African courts to be invalid.
To be valid, the agreement must be in writing and signed by the client and the attorney. Also, the client must understand the meaning of the agreement and be informed of any other fees for which he or she may be liable.
For the best legal support and representation, contact DSC Attorneys. The firm specialises in personal injury claims, including Road Accident Fund and medical negligence claims, in South Africa and works on a contingency fee basis.
See also:
(This article is provided for informational purposes only and not for the purpose of providing legal advice. For more information on the topic, please contact the author/s or the relevant provider.)